Advantages of the sensor to cloud monitoring solution
Sensor-to-cloud monitoring solution uses wireless sensor networks to capture, process, and reserve data in the cloud, permitting all users to access the data. They are used in many applications to collect and process critical operational data. The use of sensor-to-cloud systems includes
- Utility management
- Machine monitoring
- level monitoring
- parking management
- Energy management
Sensor-to-cloud systems help enterprises by facilitating, revving, and automating sensor data control.
WHAT IS A SENSOR-TO-CLOUD SYSTEM?
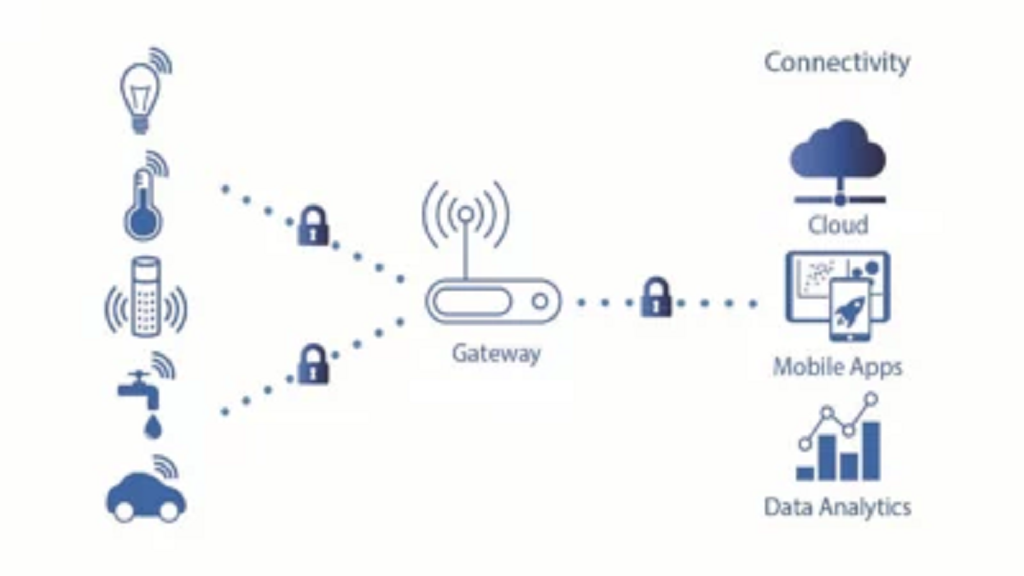
A sensor-to-cloud system merges wireless sensor networks and the cloud, extending the ability of standard networks for computing, storage, communication, and scalability.
A network of self-regulated sensors commonly operated in industrial and building applications monitor space for elements such as temperature, Humidity, pressure, vibration, proximity, and movement. Gateways then shorten and transmit this data to the cloud, where it gets decompressed and stored in the server. The sensor network contains the information, and complicated functions like data analysis and processing are also transmitted to the cloud, lessening the load on sensor networks and expediting processing time.
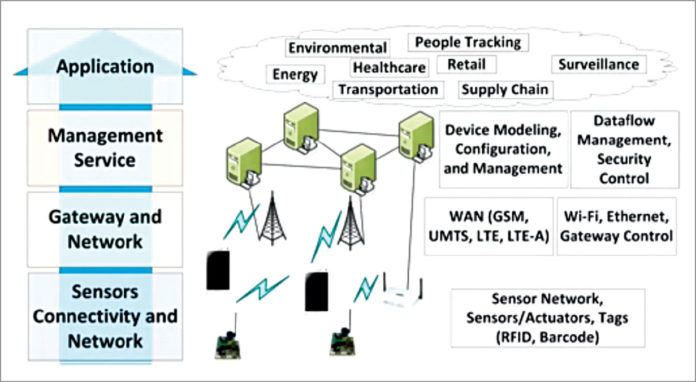
This sensor network consists of three layers.
Physical layer
This layer consists of physical sensors that collect data. Sensor Modeling Language uses XML encoding for physical sensors to implement across multiple hardware and platforms with minimal human effort.
Virtual layer
In this layer, all physical sensors are virtualized on a cloud computing platform so that users can control their physical sensors. Virtual sensors equip real-time data from their physical partners.
User interface layer
Users can view virtual sensor data sent to the cloud. Cloud computing allows data access by multiple users, potentially across numerous organizations and over different networks and OS. Users can organize data and sensors with a web-based Dashboard.
Advantages of Sensor-to-cloud systems
Sensor-cloud systems optimize sensor data management by using the cloud to collect, access, visualize, analyze, store and share large amounts of data from multiple sensors. They enhance the data management procedure by diminishing human interference. Users can explore and operate on sensor data without worrying about execution, as the cloud will automatically feed services when users send a request. Automation has grown efficiency while reducing cost and service delivery time.
Find Your Sensor-to-Cloud Solution
Drive `revived income creeks and efficiencies with actionable data using sensor-to-cloud solutions.
Analysis
Sensors collect, process, and interpret data in real time, aiding you in making smarter decisions quickly. Users can more efficiently explore large amounts of data from multiple sensor networks with sensor-cloud monitoring systems. Massive cloud storage gives you access to historical data to track trends and measure improvement.
Scalability
Because the cloud has an ample routing infrastructure, sensor networks grow at much larger scales. As enterprises grow and need more resources, they’ll be able to mount their sensor infrastructure with their firm without investing in new hardware. Also, sensor-to-cloud monitoring methods improve data repositories rather than physical computer systems, enabling growing companies to store more data as they develop without spending time and money on new hardware.
Collaboration
The cloud allows multiple parties to access data from any location, encouraging greater collaboration. Considerable physical sensor networks portray data on the cloud, making significant quantities of data readily available.
Visualization
As part of sensor-to-cloud monitoring, a visualization API represents charts based on sensor data, authorizing workers to create a sense of detailed data from multiple sensors in a network. You’ll be able to diagnose present data conventions that could have otherwise gone unrecognized to anticipate future trends.
Automation
Automation is a crucial objective of the IoT, dramatically improving productivity by delivering more rapid delivery times. In the past, workers physically controlled sensors. Automation simplifies the sensor monitoring procedure, as sensor-to-cloud lets, you grab and research data automatically. If problems arise, the system will notify the necessary individual.
Flexibility
While ex-computing procedures need hardware, sensor-to-cloud systems supply better flexibility, as you’ll be capable of using more applications to manage sensors and skillfully communicate resources and data with others across the globe via the cloud.
Multitenancy
Several service providers can combine numerous services via the cloud, allowing access to data from different origins. Although others who do not have the permit to your data cannot witness it, all data consistently run on the same server.
Security
WSN can also be used for security, noticing actions to control unauthorized access and transmitting an alert to the cloud. Door sensors detect open doors, command locking mechanisms, and even activate alarms. Window sensors operate like door sensors but frequently monitor the temperature to optimize energy consumption. Finally, motion sensors can communicate an alarm or call the authority to keep spaces like warehouses or artifacts at museums safe.
Cost
Cloud infrastructure helps with more influential computing and storage capability without the actual hardware expense. Also, you’ll be capable of monitoring devices and making the required rehabilitation before they evolve too pricey.
Installation
One of the essential edges of wireless sensors is that they are fast and easy to establish. The technology will instantly start gathering data and transmitting it to the cloud once connected to the asset.
The Constant Growth OF Sensor to cloud methods
Like how sensor technology has developed to become wireless, sensor-to-cloud methods are continually improving for enhanced capabilities and security. Coming enhancements include:
- Developed applications: Future developments in WSN technology will forge sensor applications for underwater acoustic techniques, cognitive sensing, and instances where the period is critical.
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning: Combining artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) with sensor-to-cloud systems to expedite data collection and monitoring via further mechanization.
- Improved security: Some individuals have raised safety problems with WSNs and cloud computing. Forthcoming developments will preserve the integrity of nodes to ensure that damages don’t compromise the system. Experimenters propose a three-layer data storage scheme to improve future security.
CONNECT WITH BRIDGE THINGS, A MULTI-TECH BRAND, FOR WIRELESS SENSORS
BridgeThings is the top manufacturer of Long Range Wide Area Network (LoRaWAN®) sensors for Internet of Things (IoT) systems in India and worldwide. Our long-range and low-cost sensors have an impressive battery life to monitor temperature, Humidity, movement, air quality, and water leaks. Contact us today to learn more about our wireless sensor solutions.