Wireless technologies play a crucial role in building complex IoT applications. In today’s IoT ecosystem, there are models of wireless technologies, such as LAN, WAN, LPWAN solutions, and each has additional features and specifications for various use cases.
LAN-Local Area Network
WAN-Wide Area Network
LPWAN- Low Power Wide Area Network
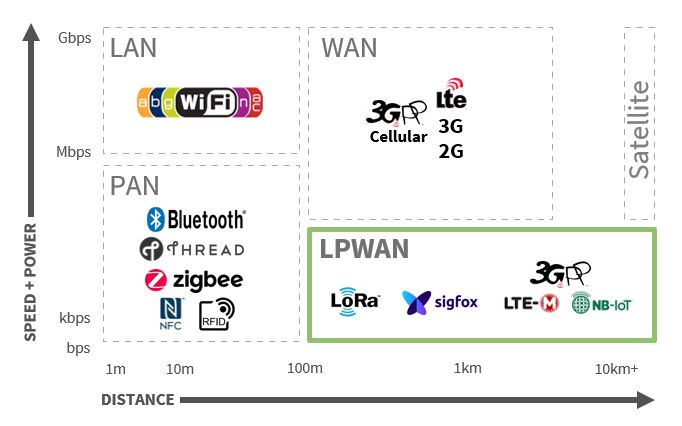
These distinct types of wireless technologies differ in distance, transmission rate, and power consumption. In this study, we are going to add one of the wireless technologies in IoT– LPWAN. This class of wireless technology is used in extended coverage and long-distance communications, as it enables long-range transmissions.
What is LPWAN?
LPWAN Low power wide area network is a type of wireless technology, and it requires low power, has extended operating ranges, and typically transmits a limited amount of data per day. Organizations are looking to reduce the manufacturing and lifetime operating costs of IoT devices select LPWANs. it Can accumulate data from a different device, For example, Sensor., meters or gauges
Sensors are linked to form a communication network, and all data forwarded to a cloud platform
LPWAN Features
- wide area-long distance transmission
- low -power consumption
- Security and privacy
LPWAN Applications
- Environmental monitoring (Air pollution, temperature, humidity)
- Smart meter reading (water, electricity, gas)
- smart Agriculture(water quality, Ph level, oxygen levels)
- Real-time traffic control systems
- management of parking spaces in parking lots
While some stories are shared, others are available only with precise solutions. It’s, therefore, necessary to assess all of them to recognize
which fits your requirements. Below we have a smart review of LPWAN Technologies.
LoRaWAN (Long-Range Wide Area Network)
LoRaWAN uses gateways to send messages, connecting devices, and network servers. These gateways adjust the radio frequency packets they receive from endpoints into IP packets that travel over the network.
A LoRaWAN network server maximizes network size and battery life by using adaptive data rate (ADR), allowing for a dynamic tradeoff between communication range and message duration for each endpoint individually. Among LoRaWAN’s key benefits are:
- A comprehensive coverage range between Five and Fifteen kilometers, with shorter ovens in urban areas
- A single gateway can manage multiple IoT devices or End nodes.
- Widely used solution for IoT applications
- By using the Adaptive Data Rate Technique, we can increase battery life and Network capacity
Organizations should consider LoRaWAN when:
- An extensive coverage range is required.
- Data rates above 27 Kbps are not necessary.
- Latency is not an obstacle: No real-time or Crucial applications
- The limited time during which the channel occupies (duty cycle) will not interfere with the essential operations of the device.
NB-IoT (NarrowBand Internet of Things)
NB-IoT is Low Power wide Area network Lpwan Technology invented to decrease power consumption and boosts system function and spectrum efficiency, especially in underground and remote locations. NB-IoT Key
selling point is price savings derived from two factors: Lack of complexity in the underlying technology and its absence of need for a cellular gateway to the whole and transmits sensor data. NB-IoT key benefits are :
- Lower device manufacturing costs determined from simple construction and leveraging chipsets specifically engineered for NB_IoT.
- Power ability due to its simpler waveform and the ability to “sleep” when not in use.
- Strong coverage under urban environments.
- Reliable coverage Under Urban Environments
- Reliability and Assured quality of service obtained by performing within an authorized spectrum.
- It supports large numbers of devices over a wide geographic area
- A simple implementation is achieved by installing on current networks and leveraging existing cellular infrastructures
- A Simple Implementation is accomplished by installing on Current networks and leveraging present cellular bases
Industries should consider NB-IoT when:
- The device will be placed in underground or hard-to-access locations.
- It doesn’t require mobility.
- It will not need the high bandwidth necessary to transfer large amounts of data, including large files, voice, or video.
- It will require an extended battery life.
- A highly scalable solution is needed to handle an extensive network of sensors.
When is LPWAN the right choice?
Choosing the right connectivity technology is always tricky. IOTS have Distinct options and LPWAn is one Type of wireless technology LPWAN Low power wide area Network Technology is the best choice when devices or sensors are located underground, in remote areas or deep with urban support, and the primary application for LPWAN’S include smart water metering, gas and fule detectors, smart lighting, and smart agriculture.